What makes Parmigiano Reggiano so unique?
The secret is to transfer the tasty bacteria from the grass, to the cow, to the milk.
It can then impart its delicious flavor on the cheese.
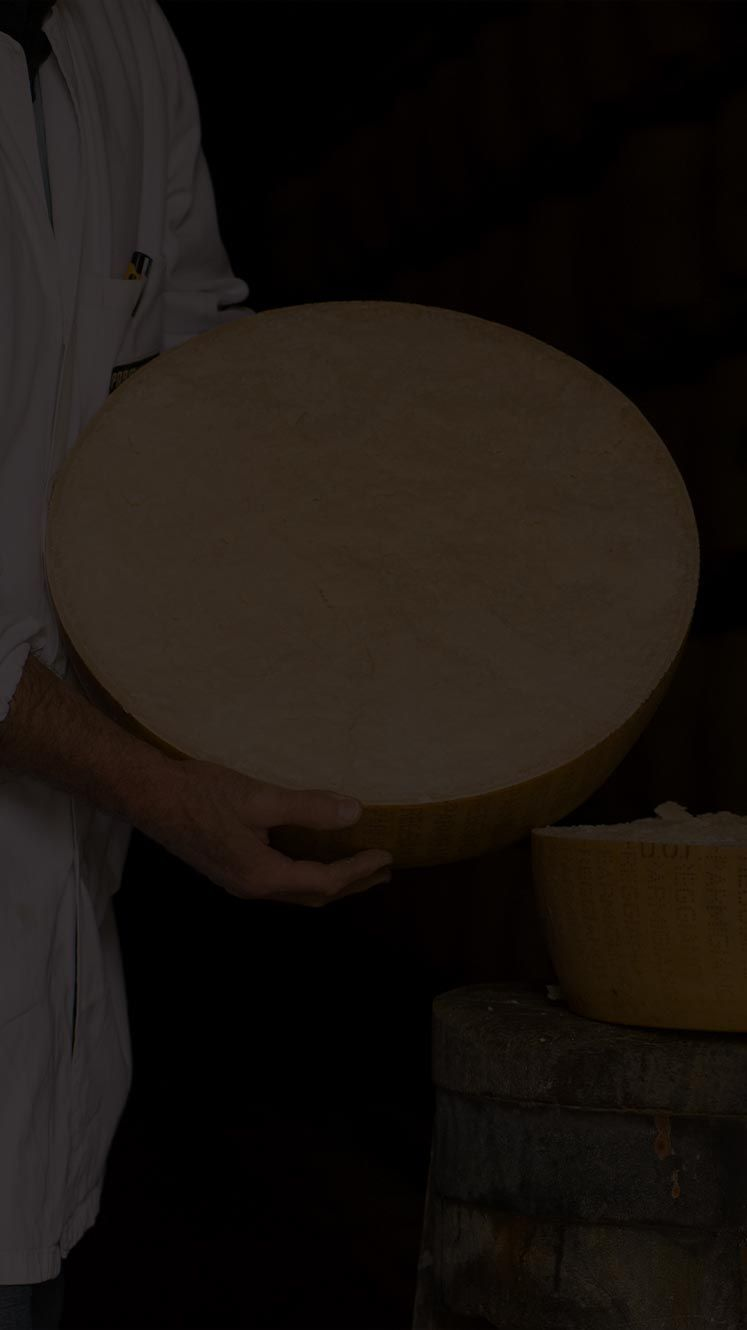
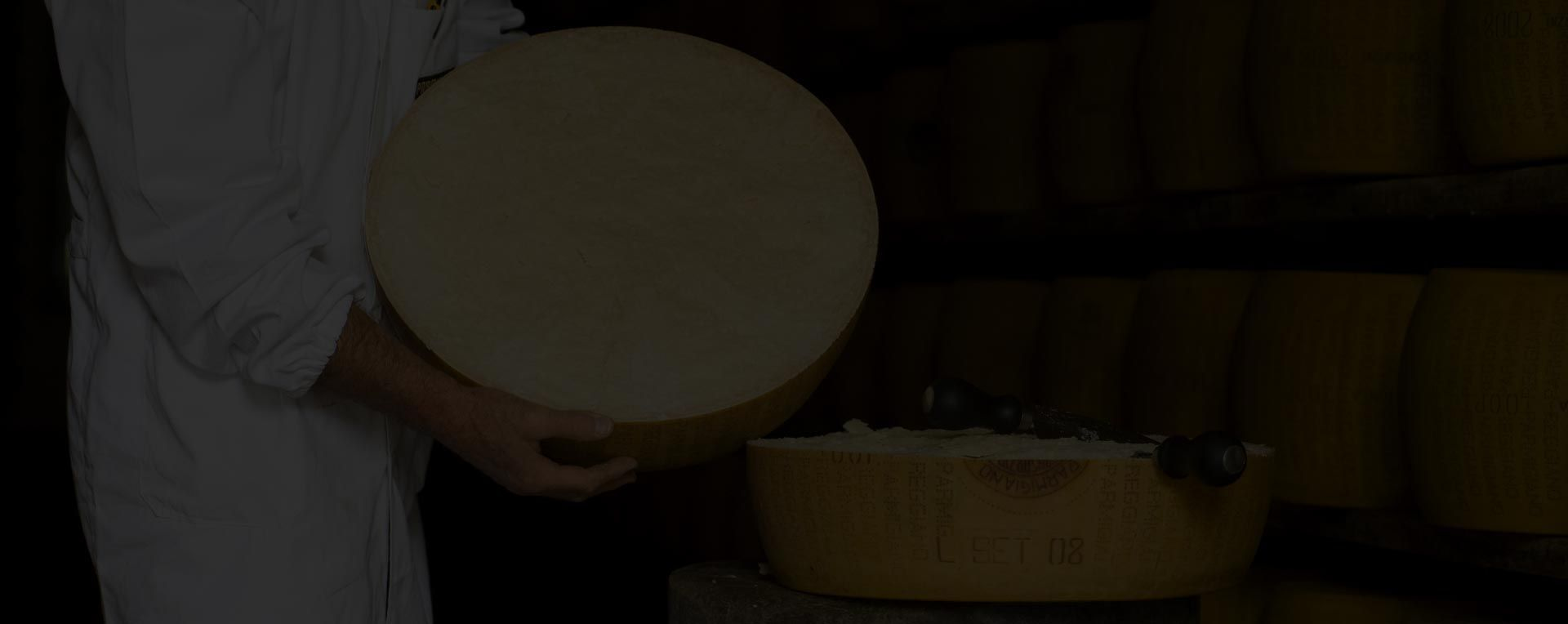


Parmigiano Reggiano and Grana Padano
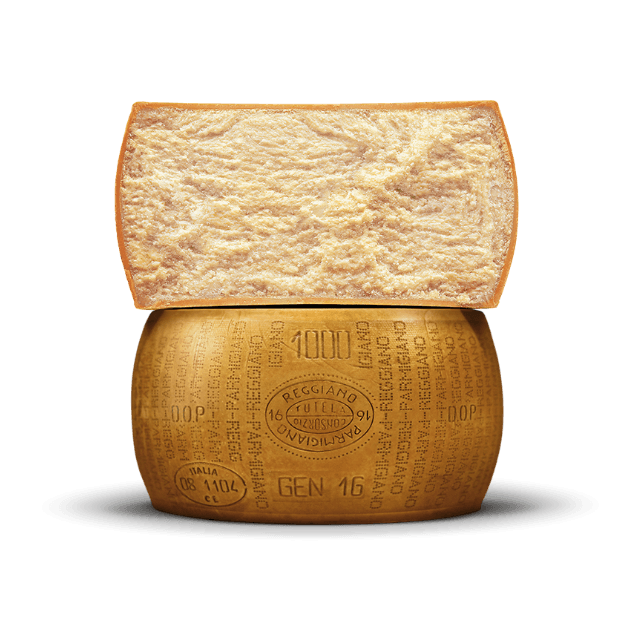

What makes Parmigiano Reggiano so unique?
The secret is to transfer the tasty bacteria from the grass, to the cow, to the milk.
It can then impart its delicious flavor on the cheese.
The differences between Parmigiano Reggiano and Grana Padano
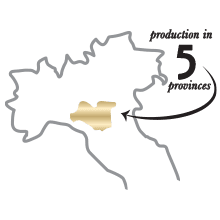
Production in 5 provinces
The production area of Parmigiano Reggiano is more localized, occurring in the provinces of Parma, Reggio Emilia and Modena and in part of Mantua (to the right of the Po River) and Bologna (to the left of the Reno River).
By contrast, Grana Padano can be produced from farms located in 33 provinces between Lombardy, Veneto, Piedmont, Emilia-Romagna and Trentino Alto Adige (limited to the province of Trento and some municipalities in the province of Bolzano).

NO additives
Parmigiano Reggiano is made with no additives and its production specifications also prohibit the use of natural additives.
However, Grana Padano allows the use of lysozyme, a protein extracted from hen’s egg white, to control unwanted fermentation.

ONLY hay and grass
To make Parmigiano Reggiano, cows are exclusively fed hay and grass (alfalfa and stable meadows), without using silage or fermented forage.
Grana Padano allows the use of silage in the feed.

Minimum and average maturation
The minimum maturation period for Parmigiano Reggiano is 12 months and, although the average maturation period is 24 months, the cheese can be matured for much longer – even up to 30 months and beyond.
Grana Padano is marked at 9 months and on average consumed at 15 months.

ONLY natural fermented whey
Parmigiano Reggiano dairies exclusively use natural fermented whey as a bacterial starter to boost the microbiological process.
Grana Padano allows the use of lactic bacteria isolated in a laboratory from dairies’ natural fermented whey, albeit this is limited to 12 times per year.
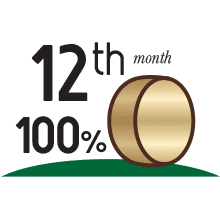
Quality inspection
Parmigiano Reggiano boasts a 100% quality-control rate as the selection carried out by the Consortium during quality inspection (suitability assessment) at 12 months is performed on every single wheel.
For Grana Padano, such a selection only occurs at 9 months and only on some wheels.
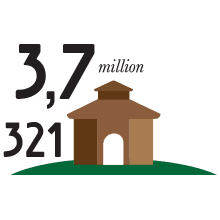
Dairies and annual production
In 2019, 3,754,192 wheels of Parmigiano Reggiano were produced in 321 dairies, while 5,164,59 wheels of Grana Padano were produced in 128 dairies.